The term “Geometry” comes from the Greek words “Geo,” meaning Earth, and “Metron,” meaning Measurement. This translates to “Earth’s Measurement,” and geometry primarily focuses on the properties and relations of figures and shapes. In practice, it is crucial for calculating areas, volumes, and lengths. Euclid, often called the “Father of Geometry,” is a key figure in its development.
From birth, humans are naturally drawn to various shapes, designs, and colors. This is evident in everyday life, where people are attracted to products such as fabrics with interesting patterns, books with eye-catching covers, uniquely shaped sunglasses, jewelry with captivating designs, and beautifully crafted mugs, among many others. Geometry is truly “omnipresent.” Additionally, geometric shapes in toys play a significant role in the cognitive development of children during their early years. Let’s explore some important examples of geometry that play a crucial role in our daily lives.
1. Nature
The most important example of geometry in everyday life is formed by the nature surrounding humans. If one looks closely, one might find different geometrical shapes and patterns in leaves, flowers, stems, roots, bark, and the list goes on. The organisation of the human digestive system as a tube within a tube also ascertains the role of geometry. The leaves on the trees are of varying shapes, sizes, and symmetries. Different fruits and vegetables have different geometrical shapes; take the example of orange, it is a sphere and after peeling it, one might notice how the individual slices form the perfect sphere.
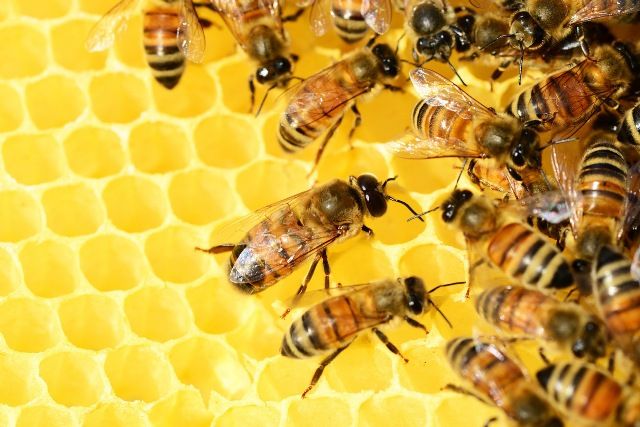
Looking closely at a honeycomb, one will see hexagonal patterns arranged tandemly. Similarly, examining a snowflake under a microscope will enable the examiner to be the guest of beautiful geometrical patterns.
The next interesting example of the role of geometry in nature is formed by the pattern popularly known as “Six-Around-One.” The flowers exhibit the “six-around-one” patterns, also called “Closest Packing of Circles,” “Hexagonal Packaging,” and “Tessellating Hexagons.”
2. Technology
The most common example of geometry in everyday life is technology. Be it robotics or computers or video games, geometry is applied to almost all the underlying concepts. The computer programmers are able to work because the concepts of geometry are always at their disposal. The virtual world of video games is created only because the geometric computations help in designing of the complex graphics of the video games. Raycasting, the process of shooting, employs a 2-D map for stimulating the 3-D world of the video games. Raycasting helps in increasing processing as the calculations are carried out for the vertical lines on the screen.
3. Homes
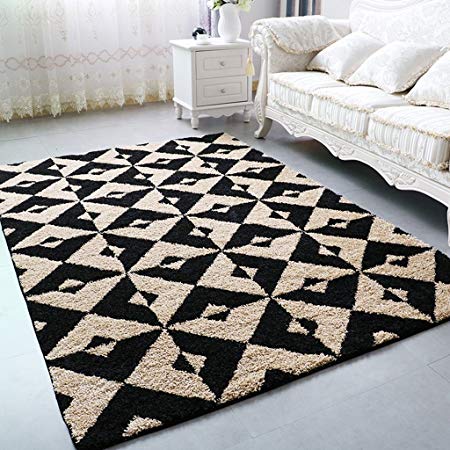
Geometry does not leave even a single chance to play a significant in homes as well. The windows, doors, beds, chairs, tables, TV, mats, rugs, cushions, etc have different shapes. Moreover, bedsheets, quilts, covers, mats, and carpets have different geometric patterns on them. Geometry is also important cooking. The chef needs to add all the ingredients in accurate proportions and ratio to put forth a delicious dish. Also, while organising a room, each and every space is utilised to make the room look more appealing. A house is made to look more presentable by using vases, paintings, and various decorative pieces, which are of different geometric shapes and have different patterns made on them.
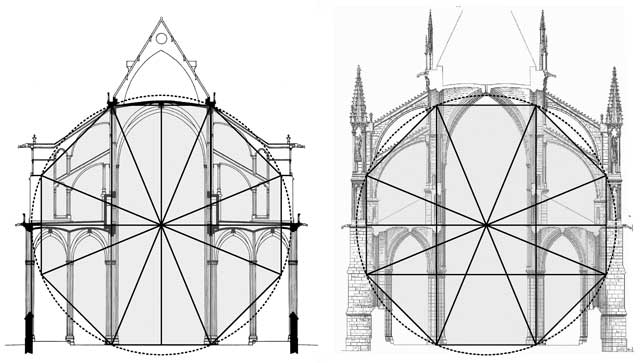
4. Architecture
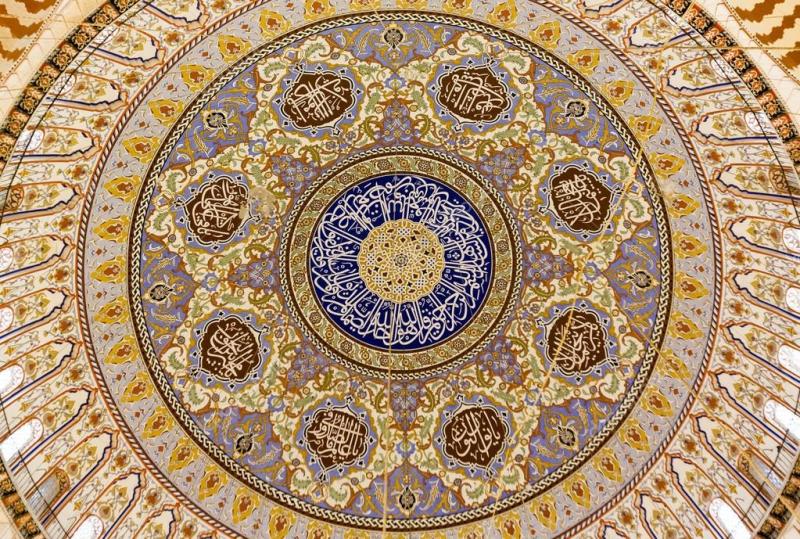
The construction of various buildings or monuments has a close relationship with geometry. Before constructing architectural forms, mathematics and geometry help put forth the structural blueprint of the building. The theories of proportions and symmetries shape the fixed aspects for all kinds of architectural designs. Pythagoras’ “Principles of Harmony” along with geometry were employed in the architectural designs of sixth century BC. Not only were the basics of mathematics coupled with geometry helped in increasing the aesthetics, harmony, and the religious value of large structures but also aided in mitigating various hazards resulting from high-speed winds.
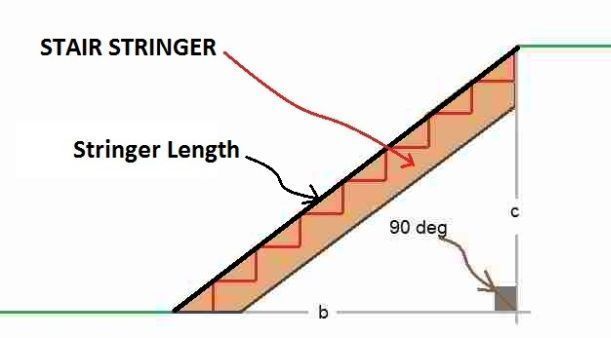
Moreover, the staircase in all the buildings take into consideration the angles of geometry and are constructed at 90 degrees.
5. Art
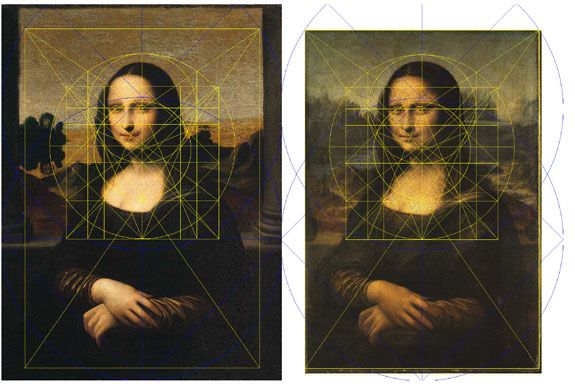
Art includes the creation of figures and shapes, an understanding of both two-dimensional (2-D) and three-dimensional (3-D) designs, as well as knowledge of spatial concepts like distance and position. It also involves estimation, patterns, and measurements. From this, it’s clear that art and geometry are closely related. When artists create shapes, they often use geometric forms like circles, triangles, squares, mandalas, or octagons. Additionally, the frames around paintings or sculptures, and their shapes, can greatly impact how the artwork is perceived. It’s also worth mentioning that the principles of projective geometry, which are used to create a sense of depth and distance, are the basis for perspective in most paintings. This perspective helps to give paintings a realistic look by making objects appear closer or farther away.
6. Sports
Sports often does not fail a sole chance to make use of geometrical concepts. The buildings of the sports stadiums and athletic fields take into consideration geometric shapes. The athletic fields also employ geometry; hockey, soccer, basketball, and football fields are rectangular in shape. The corner kick spots, goal posts, arcs, D-section, and centre circle are marked on the field. Similarly, the pitches of various other sports like volleyball and basketball take into consideration the geometrical aspects because these pitches have oval as well as circular arcs marked clearly. Talking of track field, semicircular shapes are often noticeable. Angles also play a critical role in predicting the movement of the players, enhancing their performance, and scoring a point.
7. Designing
Geometry is widely applied in the field of designing; the creation of animated figures in the video games require geometry. In the case of art, almost every element of designing is entwined with geometric proportions, which is used to depict a story. Taking the examples of miniature paintings and manuscript illumination, geometric principles are employed to compose the layout. Strict geometric proportions are paid attention to while forming individual letters in calligraphy. In designing, geometry has a symbolic role to play; as is evident from the carvings on the walls, roofs, and doors of various architectural marvels.
8. Computer Aided Design- CAD
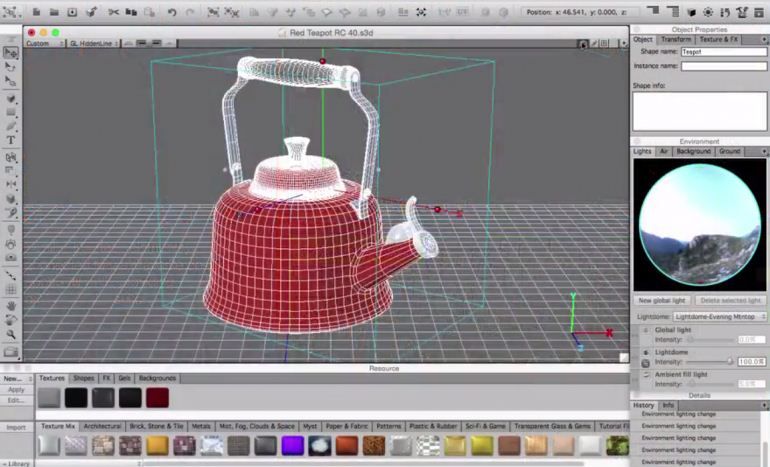
Geometry, one of the principle concepts of mathematics, entails lines, curves, shapes, and angles. Before any architectural design is made, a computer software helps in rendering visual images on the screen. CAD, a software, puts forth the blueprint of the design. Moreover, it also aids in the simulation of the architectural forms which allows for the better understanding of the finished product. The principles of geometry are being used extensively in various industrial processes which allows the designing of graphics.
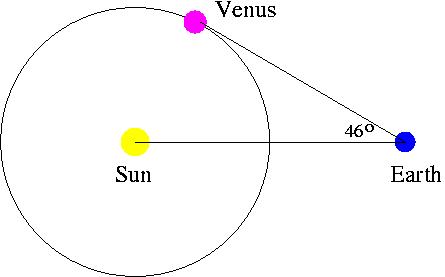
9. Mapping
Geometry helps in the accurate calculation of the physical distances. It is employed in the field of astronomy to map the distances between stars & planets and between different planets. It also aids in the determination of a relationship between the movements of different bodies in the celestial environment. Apart from mapping distances between celestial bodies, geometry also plays a vital role in surveying and navigation. In the case of surveying, measurement of the area of land is a result of the accurate determination of the shape of the land. Moreover, in navigation, the ships, watercraft, and aircraft utilise angles and also depend on other mathematical concepts for carrying out basic operations.
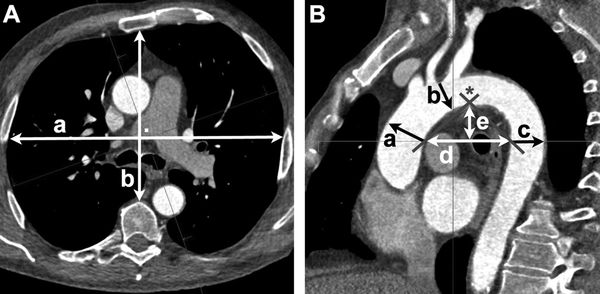
10. Medicine
Techniques like x-rays, ultrasounds, MRIs, and nuclear imaging require the reconstruction of shapes of organs, bones, and tumours, which is based on geometry only. Physiotherapy also employs geometry. Geometric properties and features help in defining the image in digital grids. The geometrical concepts not only aid in visualization, manipulation, image segmentation, correction, and object representation but also play an important role in increasing stability, fidelity, and efficiency. Bisecting angle techniques and parallel techniques are crucial in radiology.
11. Geographic Information Systems
Satellites’ GPS systems rely on geometric principles to determine their positions. The application of coordinate geometry in the Global Positioning System (GPS) enables accurate location and time tracking. By using coordinates, GPS calculates the distance between two points. Coordinate geometry also assists in tracking transportation accidents and facilitating rescue operations. Additionally, it plays a vital role in improving flight safety, weather forecasting, earthquake monitoring, and environmental protection. Furthermore, various aspects of military operations are supported by GPS technology.
Image Sources
- https://fineartamerica.com/
- https://images-na.ssl-images-amazon.com/
- http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/
- http://s3.amazonaws.com/
- https://www.britannica.com/
- https://store.schoolspecialty.com/
- https://ak7.picdn.net/
- https://journal.eahn.org/
- https://inspectapedia.com/
- https://upload.wikimedia.org/
- https://i.all3dp.com/
- https://www.eg.bucknell.edu/